
Pseudouridine found in various types of non-coding RNAs plays a critical role in regulating their structure and function. The distribution and synthesis of pseudouridine modifications have been extensively studied in eukaryotes and bacteria, but not well understood in the third category of organisms - archaea.
In a study published in Nucleic Acids Research, a research group led by YE Keqiong from the Institute of Biophysics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has revealed for the first time the global map of RNA pseudouridine modification distribution and synthesis in the model archaeon Sulfolobus islandicus.
The researchers used high-throughput sequencing to detect pseudouridine sites on rRNA, tRNA, and sRNA in S. islandicus. In addition, using RNA immunoprecipitation sequencing (RIP-seq) methods, with the pseudouridine synthase (PUS) Cbf5 as a bait protein, six H/ACA RNAs were found in S. islandicus, including classical H/ACA RNAs and non-classical H/ACA RNAs, the latter lacking a lower stem and ACA motif. Sequence alignments revealed the presence of three PUSs in S. islandicus.
By mapping pseudouridine sites to different PUSs and performing in vivo and in vitro experiments, the researchers found that 11 sites on rRNA are guided by H/ACA RNA, and the tRNA modification sites are catalyzed by H/ACA RNP and PUS. They also discovered that Cbf5 can directly modify two non-classical H/ACA RNAs without a guide RNA.
This study provides valuable insights into the landscape of pseudouridylation in archaea. It is the first to demonstrate that non-classical archaeal H/ACA RNA can guide pseudouridine modifications and to identify pseudouridine sites in CRISPR RNA for the first time.
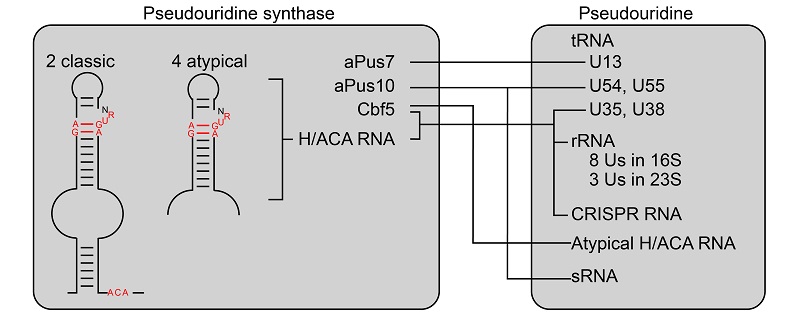
Distribution and synthesis of pseudouridine in Sulfolobus islandicus (Image by YE Keqiong's group)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

86-10-68511095 (day)
86-10-68512458 (night)

cas_en@cas.cn

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

